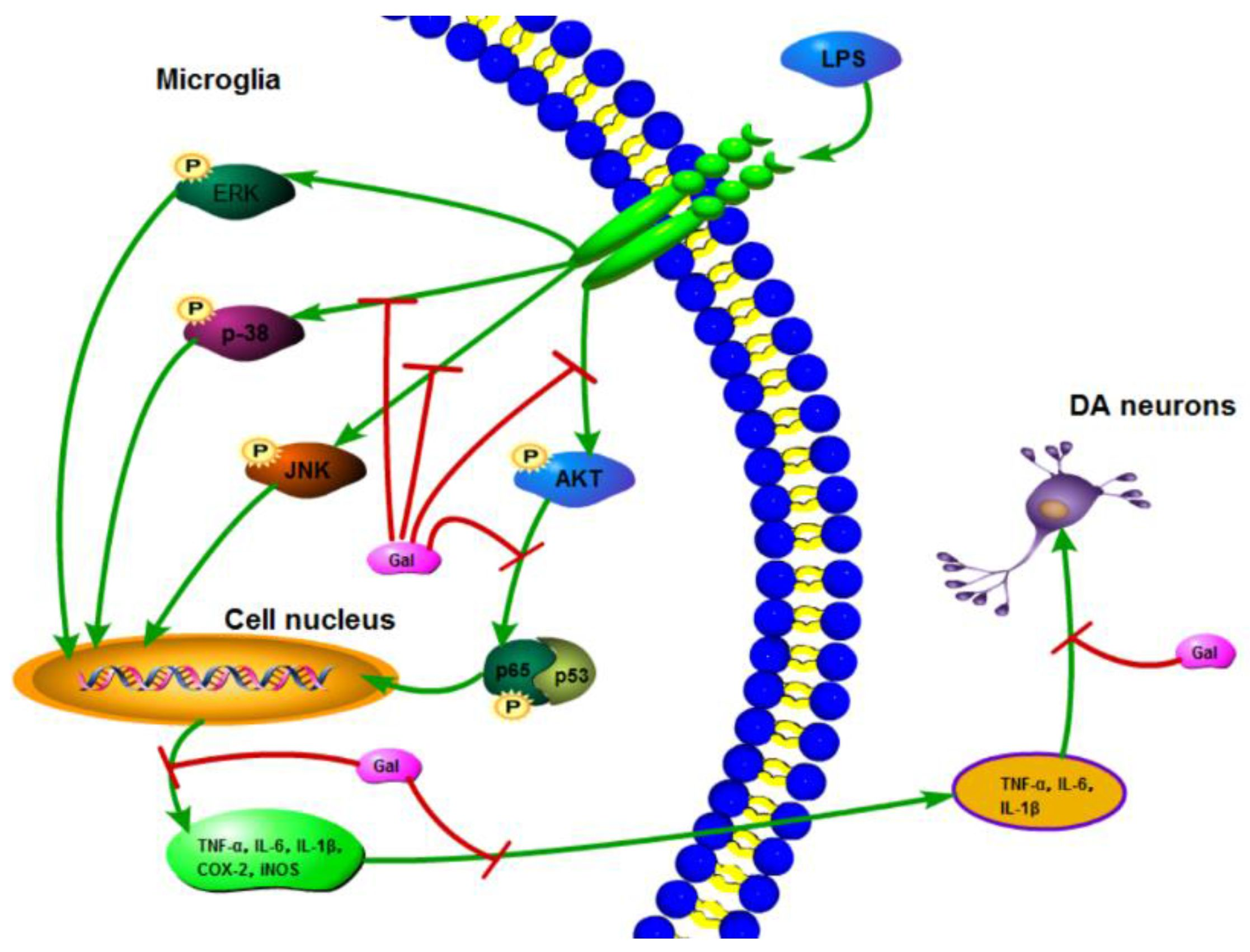
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Galangin Reduces the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in an LPS-Evoked Model of Parkinson's Disease in Rats

Perillyl Alcohol Attenuates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Rescues Dopaminergic Neurons in Experimental In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Parkinson's Disease | ACS Chemical Neuroscience

Novel compound FLZ alleviates rotenone-induced PD mouse model by suppressing TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway through microbiota–gut–brain axis - ScienceDirect

The Effects of Novel Formulations of Edaravone and Curcumin in the Mouse Intrastriatal Lipopolysaccharide Model of Parkinson's Disease
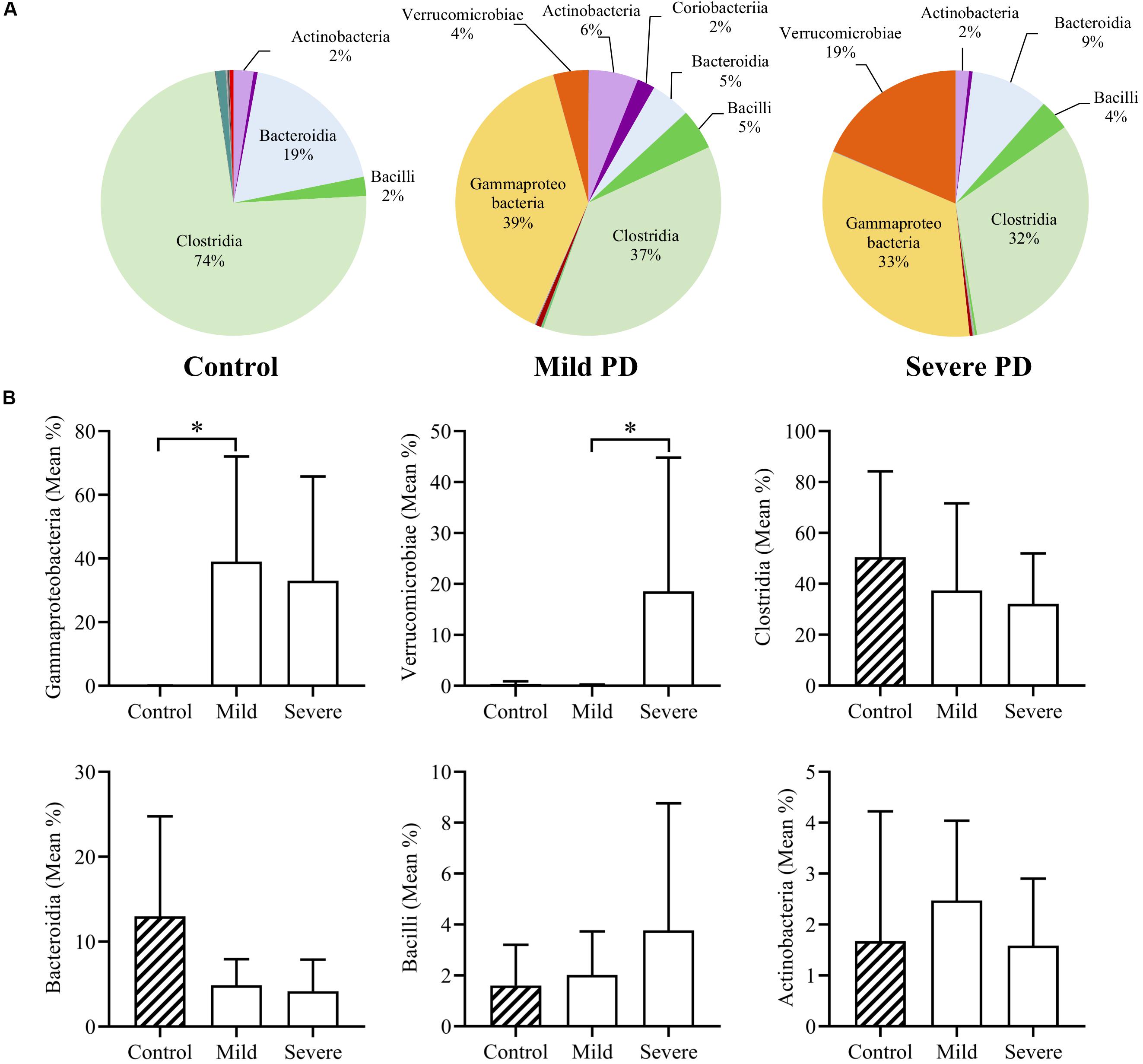
Frontiers | Altered Gut Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease and the Influence of Lipopolysaccharide in a Human α-Synuclein Over-Expressing Mouse Model
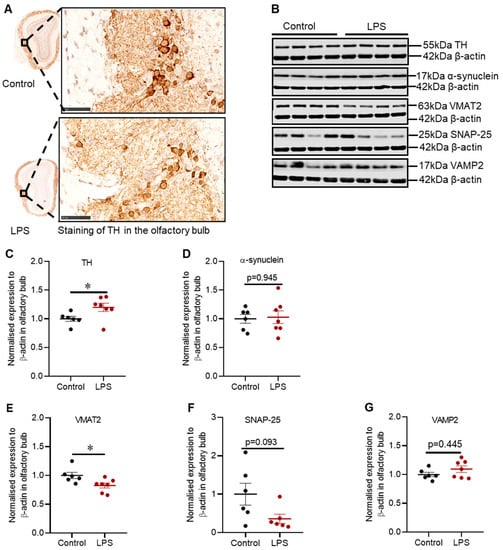
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Further Characterization of Intrastriatal Lipopolysaccharide Model of Parkinson's Disease in C57BL/6 Mice
Intranasal LPS-Mediated Parkinson's Model Challenges the Pathogenesis of Nasal Cavity and Environmental Toxins | PLOS ONE
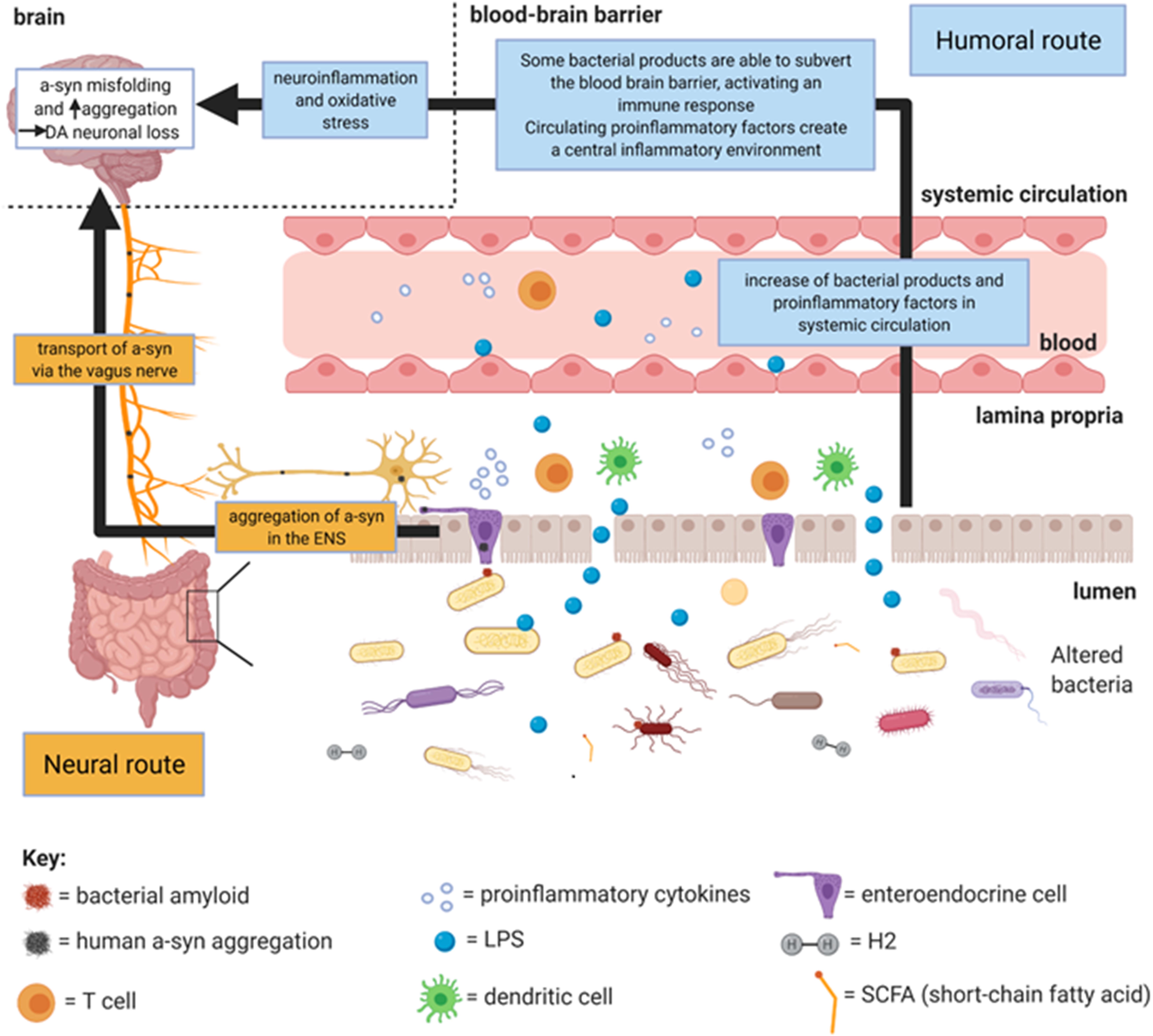
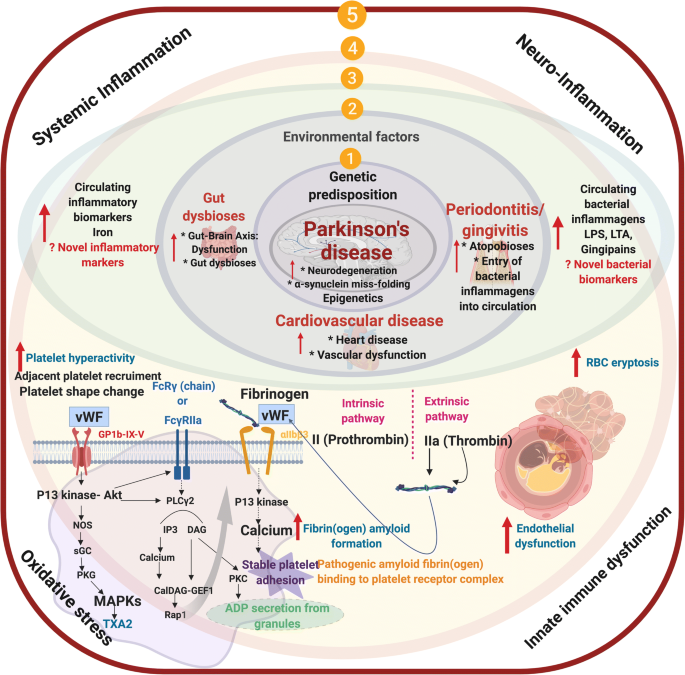
Frontiers | What Is Our Understanding of the Influence of Gut Microbiota on the Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Disease?

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease - ScienceDirect

Inflammatory Animal Model for Parkinson's Disease: The Intranigral Injection of LPS Induced the Inflammatory Process along with the Selective Degeneration of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease - ScienceDirect

Pramipexole inhibits astrocytic NLRP3 inflammasome activation via Drd3-dependent autophagy in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
Intranasal LPS-Mediated Parkinson's Model Challenges the Pathogenesis of Nasal Cavity and Environmental Toxins | PLOS ONE

Barbigerone Potentially Alleviates Rotenone-Activated Parkinson's Disease in a Rodent Model by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammatory Cytokines | ACS Omega
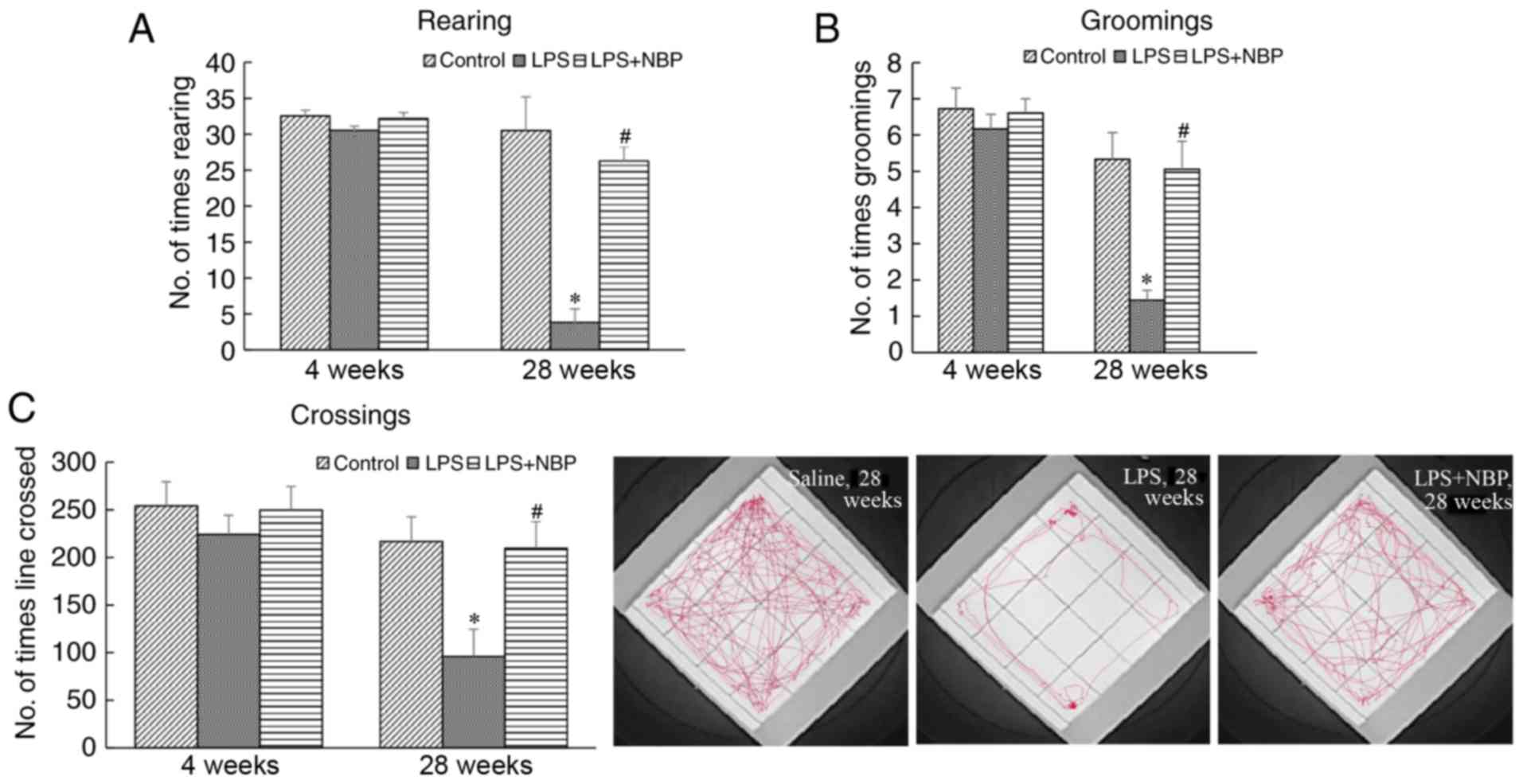
DL‑3‑n‑butylphthalide reduces microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide‑induced Parkinson's disease model mice

PDF) Inflammatory Animal Model for Parkinson's Disease: The Intranigral Injection of LPS Induced the Inflammatory Process along with the Selective Degeneration of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons

Osmotin attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairments via the TLR4/NFκB signaling pathway | Scientific Reports
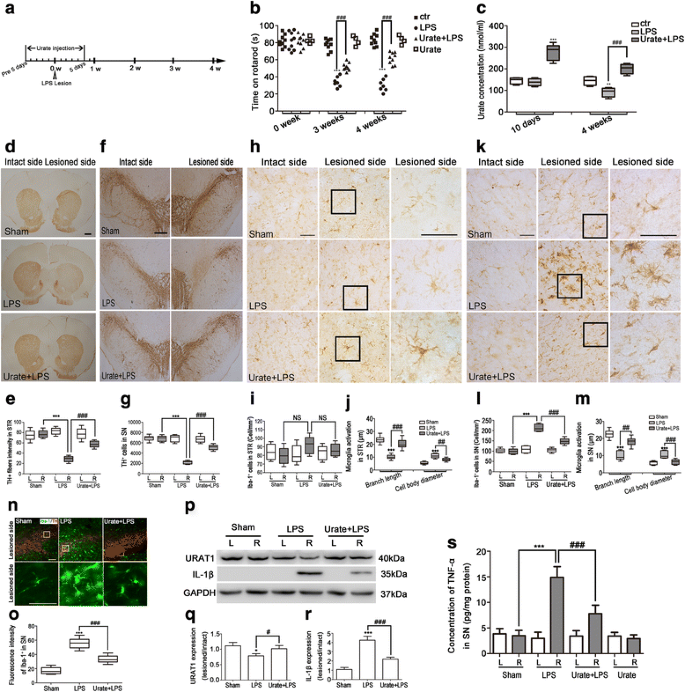
Urate inhibits microglia activation to protect neurons in an LPS-induced model of Parkinson's disease | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text

Parkinson's Disease-Related Proteins PINK1 and Parkin Repress Mitochondrial Antigen Presentation: Cell


![PDF] Lipopolysaccharide Animal Models for Parkinson's Disease | Semantic Scholar PDF] Lipopolysaccharide Animal Models for Parkinson's Disease | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a63c762e0fa3c8d5b24bb90bbf75a3ae3fff0174/6-Figure1-1.png)